- Konu Başlıkları
- Breaking Down the Core Components
- Extruder: Precision in Material Deposition
- Print Bed: The Foundation for Stability
- Frame and Structure: Ensuring Rigidity
- Control Board: The Command Center
- Material Science: The Backbone of Component Production
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
- Practical Tips for Technicians and Hobbyists
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What materials are used in 3D printer components?
- How are components tested for quality?
- Can hobbyists replace components themselves?
- Conclusion: The Anatomy of a 3D Printer: Key Components & Their Production
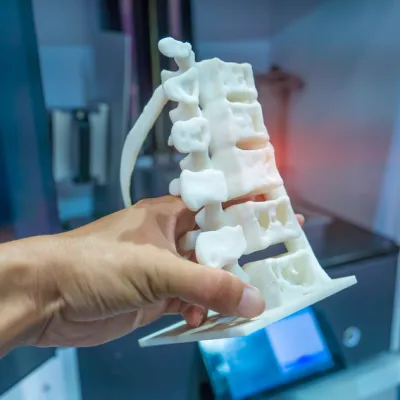
3D printing has transformed industries, empowering engineers, hobbyists, and manufacturers to create intricate designs with precision. The backbone of this technology lies in the interplay of 3D printer components, each crafted with meticulous care to ensure seamless performance. This guide explores the anatomy of a 3D printer, detailing the production and integration of its key parts, enriched with material science insights and expertise from Erlas Global, a pioneer in 3D production since 1984.
Breaking Down the Core Components
A 3D printer’s functionality hinges on its core components, each serving a unique purpose in transforming digital models into tangible objects. Understanding their roles and how they are produced offers valuable insights for students, technicians, and aspiring manufacturers.
[widget-131]
Extruder: Precision in Material Deposition
The extruder is the heart of a 3D printer, melting and depositing filament with pinpoint accuracy. Comprising a nozzle, heater, and filament drive, it requires precision engineering to maintain consistent flow and temperature.
- Materials: Stainless steel or brass nozzles ensure durability and thermal conductivity.
- Production: CNC machining achieves tight tolerances, while ceramics provide heat insulation. Erlas Global’s expertise in precision manufacturing ensures extruders withstand high temperatures.
- Expert Tip: Regular nozzle maintenance prevents clogs and extends component life.
Print Bed: The Foundation for Stability
The print bed provides a stable surface for printing, requiring flatness and temperature consistency to prevent warping. Materials like aluminum or borosilicate glass are chosen for their thermal properties.
Manufacturing print beds involves advanced techniques to ensure durability. For instance, laser cutting creates smooth surfaces, while coatings like PEI enhance adhesion. These processes reflect the high standards seen in broader 3D printing applications, where precision is paramount.
Frame and Structure: Ensuring Rigidity
The frame anchors the printer, minimizing vibrations to ensure precise movements. Typically made from aluminum or steel, frames are produced using CNC machining or laser cutting for accuracy.
- Production Insight: Erlas Global employs advanced welding techniques to create robust frames.
- Sustainability: Recycled aluminum reduces environmental impact without compromising strength.
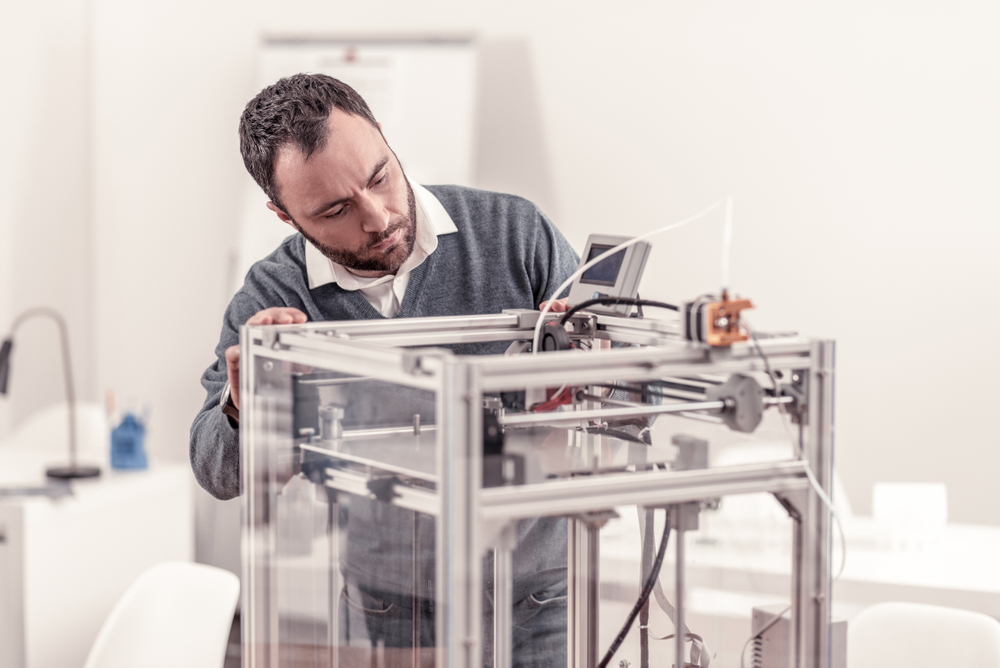

Control Board: The Command Center
The control board orchestrates the printer’s operations, managing motors, sensors, and temperatures. Produced using surface-mount technology (SMT), these boards are compact yet powerful.
Custom firmware can optimize performance, as seen in Erlas Global’s approach to tailoring control systems for specific prototype production needs, ensuring reliability in demanding applications.
Material Science: The Backbone of Component Production
Material selection in 3D printer production is a balancing act of durability, thermal resistance, and cost. Nozzles demand high-grade stainless steel to resist wear, while print beds leverage borosilicate glass for thermal stability.
- Thermoplastics: ABS and PLA filaments require specific extruder designs for optimal performance.
- Metals: Aluminum and steel provide structural integrity with excellent strength-to-weight ratios.
- Ceramics: High-temperature zones like the extruder benefit from ceramic insulation.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Producing 3D printer components requires cutting-edge manufacturing processes to achieve precision and reliability. Key methods include:
- CNC Machining: Delivers micron-level accuracy for extruders and frames.
- Laser Cutting: Ensures smooth, precise cuts for print beds and panels.
- Injection Molding: Ideal for mass-producing smaller parts like gears.
Practical Tips for Technicians and Hobbyists
For repair technicians and hobbyists, understanding component production aids in maintenance and upgrades. For example, replacing an extruder requires matching nozzle materials to filament types, while print bed calibration ensures adhesion and prevents warping.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What materials are used in 3D printer components?
Stainless steel, aluminum, borosilicate glass, and ceramics are common, selected for durability and thermal performance.
How are components tested for quality?
Stress testing, thermal analysis, and precision checks ensure reliability. Erlas Global adheres to ISO-compliant quality standards.
Can hobbyists replace components themselves?
With technical knowledge, extruders and print beds can be replaced, but complex repairs may require professional assistance.
[widget-136]
Conclusion: The Anatomy of a 3D Printer: Key Components & Their Production
The anatomy of a 3D printer reflects a synergy of precision engineering and material science. From the extruder to the control board, each component is crafted to deliver exceptional performance. Erlas Global’s expertise in manufacturing processes ensures components meet rigorous standards. Ready to dive into 3D printing? Contact Erlas Global to transform your ideas into reality.